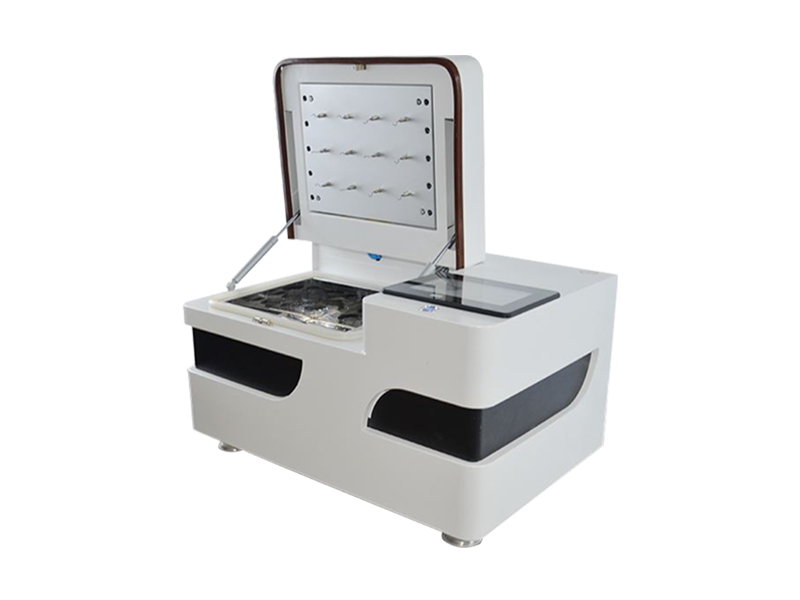
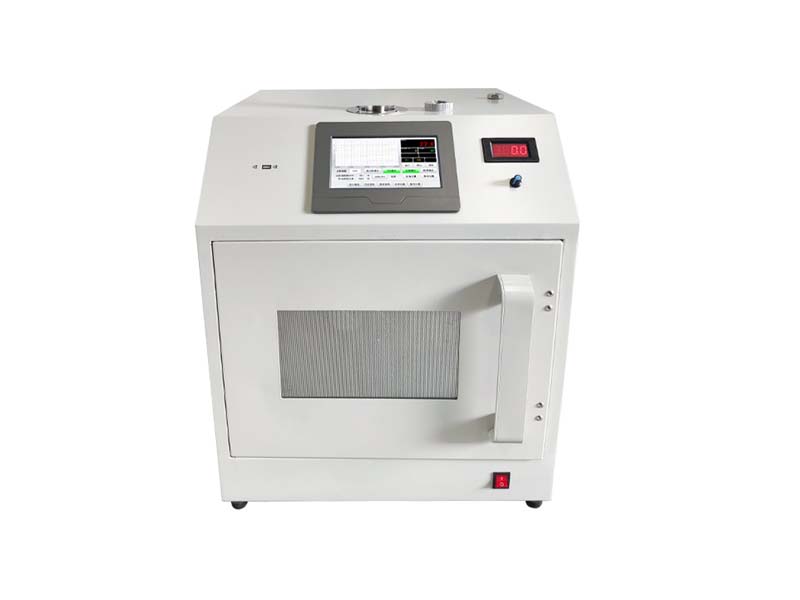
In the production process of packaging materials, solvents are inevitably used. However, excessive residual solvent levels may pose potential risks to product quality and human health. Therefore, accurate determination of residual solvent content in packaging materials is particularly important. Gas chromatography, as an efficient and accurate detection tool, is widely used to determine the residual solvent content of packaging materials. This article will provide a detailed introduction to the detection scheme of residual solvents in packaging materials using gas chromatography.

Experimental principle
A gas chromatograph is an analytical instrument that separates and detects substances based on the difference in distribution coefficients between the gas phase and the stationary phase. When determining the residual solvent content of packaging materials, the solvent in the sample is heated and vaporized in a gas chromatograph, and then separated by introducing it into the chromatographic column through a carrier gas. Different solvents have different retention times in the chromatographic column, thus achieving the separation of various solvent components. The separated solvent components enter the detector and are converted into electrical signals, and then the concentration information of each component is obtained through a data processing system.
Experimental procedure
Sample preparation: Cut the packaging material to be tested into small pieces and extract the residual solvent with an appropriate solvent. The extract is filtered, concentrated, and processed to obtain the sample to be tested.
Selection of chromatographic column: Choose the appropriate chromatographic column based on the properties of the solvent to be tested. Commonly used chromatographic columns include silica gel columns, organic polymer columns, etc.
Instrument condition setting: Set parameters such as injection port temperature, detector temperature, and column temperature of the gas chromatograph to ensure that the instrument is in working condition.
Injection detection: Inject the sample to be tested into the injection port and introduce it into the chromatographic column for separation using a carrier gas. The separated solvent components enter the detector, and the retention time and peak area of each component are recorded.
Data processing: Based on the retention time and peak area of each component, combined with standard curves or standards, calculate the concentration of each solvent component in the test sample.
Precautions
During the experiment, the experimental conditions should be strictly controlled to ensure the accuracy and reliability of the data.
Choose appropriate solvents for sample extraction and avoid using solvents that may damage the chromatographic column.
Regularly maintain and upkeep the instruments to keep them in good working condition.
Gas chromatography, as an efficient and accurate detection tool, plays an important role in the determination of solvent residues in packaging materials. Through reasonable experimental design and operation, accurate measurement results can be obtained, providing strong support for product quality control and human health protection. In practical applications, it is necessary to optimize and improve the experimental plan according to specific situations to enhance detection efficiency and accuracy.
In summary, the gas chromatography detection scheme is a reliable and effective method for determining solvent residues in packaging materials, and is worthy of widespread promotion and application in related fields.
Article address:http://www.labinstruments.net/solu/26.html