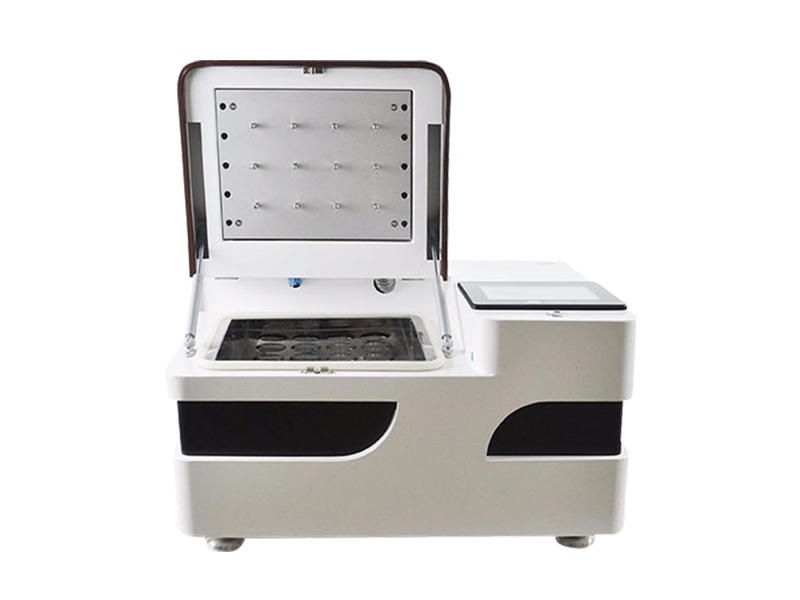
In the field of chemical analysis, titration analysis, as a classic and important quantitative analysis method, has long played a key role in quality control and scientific research. The potentiometric titrator has improved the precision and accuracy of titration analysis through automated and intelligent detection methods. As a precision analytical instrument based on the principle of potential change, the potentiometric titrator automatically determines the endpoint of titration by monitoring the changes in battery electromotive force in real-time during the titration process, effectively eliminating subjective errors caused by human judgment.
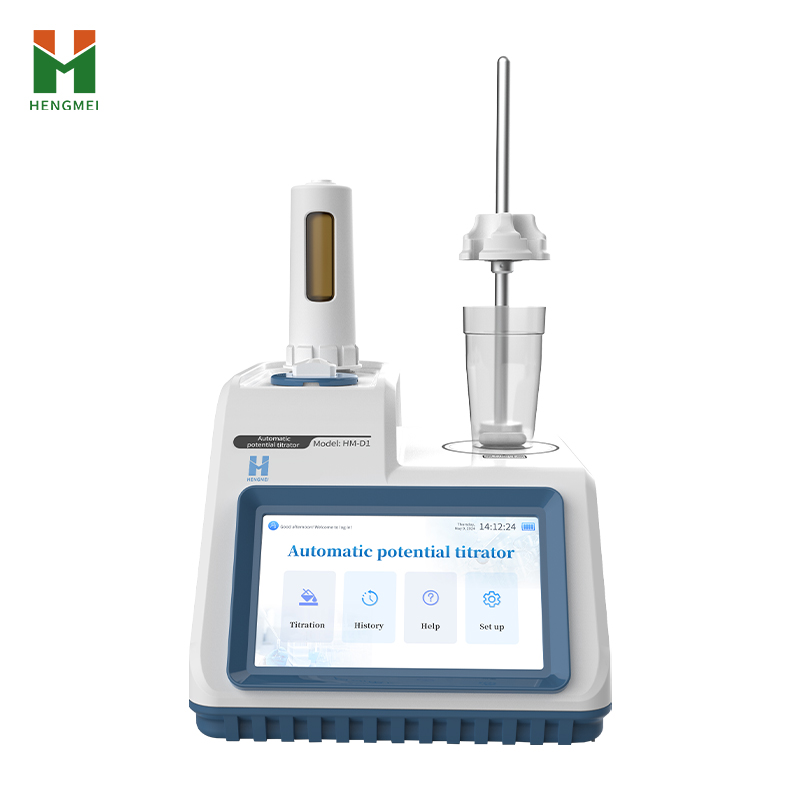

Technical principles
1. Basic principle of potentiometric titration
The core working principle of a potentiometric titrator is based on electrochemical potential measurement technology. During the titration process, the instrument tracks the reaction progress in real time by measuring the changes in electromotive force between the indicator electrode and the reference electrode. When the titration reaction reaches the stoichiometric point, the concentration of the analyte in the solution undergoes a sudden change, resulting in a sudden change in electrode potential. The potentiometric titrator captures this sudden jump point through a high-precision potentiometric sensor, automatically determines the titration endpoint, and accurately calculates the content of the analyte.
The potential measurement range equipped with the instrument covers -2000 to 2000mV, with a resolution of 0.1mV and a basic error controlled within ± 0.25 ‰ FS. This high-precision potential detection capability ensures the accuracy of endpoint judgment and provides a solid guarantee for the reliability of analysis results.
2. Multi functional detection platform
Modern potentiometric titrators integrate multiple detection modes, and users can achieve analytical methods such as acid-base titration, redox titration, precipitation titration, and complexometric titration by selecting different electrodes. The instrument supports dual functions of potentiometric titration and pH measurement, with a pH measurement range of 0-14, a resolution of 0.01pH, and a basic error of ± 0.01pH. In addition, the equipment can also be equipped with expansion modules such as conductivity titration and permanent stop titration to meet diverse analysis needs.
Technical advantages
1. Analysis accuracy
The potentiometric titrator performs outstandingly in terms of analysis accuracy, with a titration analysis repeatability of ≤ 0.2% and an analysis error of ≤ 1.5%. In terms of titration capacity accuracy, a 10mL burette achieves ± 5 μ L, while a 20mL burette achieves ± 10 μ L. This high-precision liquid delivery system ensures the accuracy and repeatability of titrant addition.
2. Operating System
The device adopts the Android 10 intelligent operating system and is equipped with a 7-inch touch screen to achieve intuitive human-computer interaction. The instrument supports three titration modes: dynamic titration, equal titration, and manual titration. Users can choose the appropriate workflow based on the characteristics of the sample. The custom calculation formula function allows users to preset calculation methods based on reaction equations, and automatically output the content of the analyte after titration is completed, greatly improving data processing efficiency.
3. Laboratory functions
The potentiometric titrator has been designed with multiple practical functions, significantly improving laboratory work efficiency. The exhaust function can eliminate pipeline bubbles and avoid titration errors; The flushing function ensures pipeline filling with minimal reagent consumption; The emptying tube function safely recovers residual liquid after the experiment is completed. These thoughtful design details reflect the instrument's deep understanding of the actual needs of the laboratory.
Application Fields
1. Food and drug quality testing
In the food and pharmaceutical industry, potentiometric titrators are used for quality inspection of raw materials and finished products. For example, in drug content determination, food acid value and peroxide value detection, instruments provide accurate and reliable data support to ensure product quality meets regulatory requirements.
2. Environmental monitoring and protection
Environmental testing agencies use potentiometric titrators to analyze various ion contents in water quality samples, providing a basis for environmental assessment and pollution control. The high-precision measurement capability of the instrument meets the strict requirements for data accuracy in environmental monitoring.
3. Chemical production control
In the chemical industry, potentiometric titrators are used for intermediate control and quality inspection in production processes. By monitoring key indicators of raw materials and products in real-time, data support is provided for process optimization and quality control.
4. Research and Teaching Applications
Higher education institutions and research institutes use potentiometric titrators for scientific research and experimental teaching. The intelligent operation and accurate measurement capability of instruments provide an advanced technological platform for scientific research innovation and talent cultivation.
As an important tool in modern analytical chemistry, potentiometric titrators provide reliable technical support for chemical analysis through their accurate measurement performance, intelligent operating system, and comprehensive laboratory functions. This instrument not only solves the problems of subjectivity and low efficiency in traditional titration methods, but also provides important technical support for quality control and scientific research.
Article address:http://www.labinstruments.net/news/79.html